

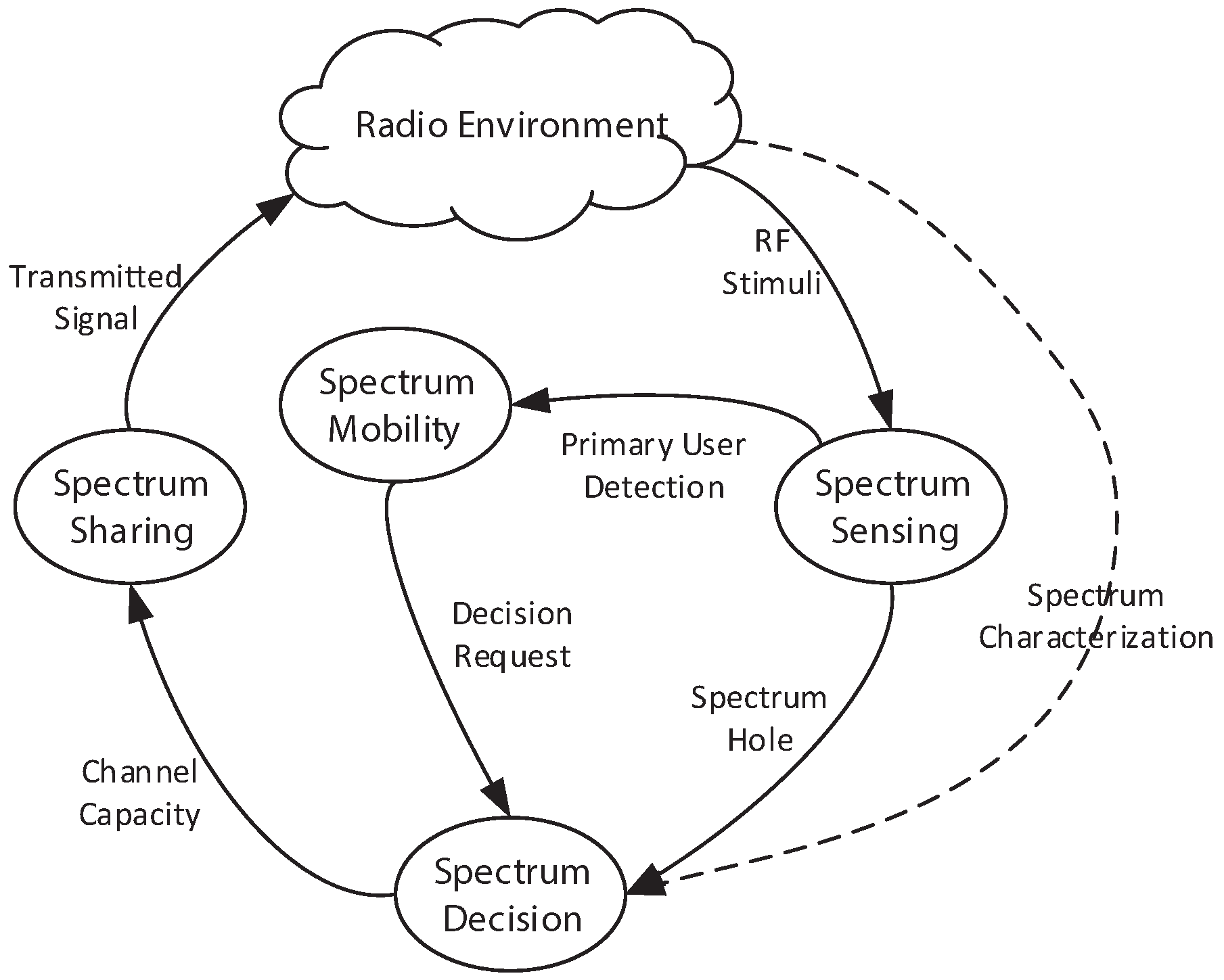
Artificial Neural network (ANN) an intelligent learning technique is used which works to improving. In this article a cognitive spectrum allocation procedure is proposed. Finally, we present an optimization framework for end-to-end flow level scheduling of flows in network with mutually interfering links. Opportunistic Spectrum Access (OSA) 1 has been en-. last years, Cognitive radio (CR) has emerged as an efficient technology to exploit the unused available spectrum resources it can sense and use spectrum in an opportunistic manner without creating any harm to cognitive users. We then present a distributed algorithm where each link independently updates its transmission probability based on its measured throughput to achieve any desired feasible rate vector in the throughput region of the probabilistic scheme and prove its convergence. We observe that for the case of two interfering links, the probabilistic scheme does not suffer any loss in the rate region relative to the centralized scheme if the interference between the links is sufficiently low. Irwin and Joan Professor in Engineering, Cornell University - Cited by 27,402 - Energy and power systems - statistical inference and learning - communications and networking. We then compare the throughput regions of centralized scheduling and a probabilistic random access scheme, wherein in each slot, a link is active with a fixed probability chosen independent of other interfering links. With knowledge of the link gains in the network, the spectrum server schedules the on/off periods of the links so as to satisfy constraints on link fairness. In the centralized scheduling framework, a spectrum server coordinates the transmissions of a group of links sharing a common spectrum. In this chapter, we present an optimization framework for link level and flow level scheduling in cognitive radio networks.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
